Table of Contents
Starting a business is a rewarding yet challenging endeavor. Whether you’re driven by a passion for a product, a desire for financial independence, or simply the idea of being your own boss, taking the leap into entrepreneurship requires careful planning and strategic execution. This beginner’s guide will walk you through each step, from developing your initial idea to successfully launching your business. By following these steps, you can turn your vision into a reality and set the foundation for long-term success.
Develop Your Business Idea
Every successful business begins with a great idea. But it’s not enough to have just any idea—it needs to be viable, sustainable, and marketable. The first step is to refine your concept and ensure there’s demand for your product or service.
Identify a Market Need
Start by identifying a problem or need within your chosen industry. Are there gaps in the market that your business could fill? Consider what your ideal customers struggle with and how your business can provide a unique solution. Use online tools like Google Trends, social media, and industry forums to discover what people are talking about and searching for.

Research the Competition
Take time to research other businesses offering similar products or services. What are they doing right? Where are their weak points? Understanding your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses can help you find a unique angle for your own business and identify areas where you can stand out.
Align Your Passion with Profitability
Starting a business is a long-term commitment, so it’s important to choose something you’re passionate about. At the same time, your idea should be financially viable. Evaluate whether there’s enough demand and potential profitability in your chosen niche before moving forward.
Write a Business Plan
A solid business plan serves as the roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, target market, financial projections, and the steps you’ll take to achieve them. This document is essential not just for keeping you focused, but also for attracting potential investors or securing loans.
Executive Summary
Start your business plan with an executive summary—a brief overview of your business, including its purpose, mission, and key goals. This section should be compelling and to the point, as it sets the stage for the rest of your plan.
Market Analysis
Analyze your industry, target market, and competition. Define your ideal customer, their needs, and how your business will serve them better than existing solutions. This analysis will inform your marketing strategy and help you position your brand effectively.
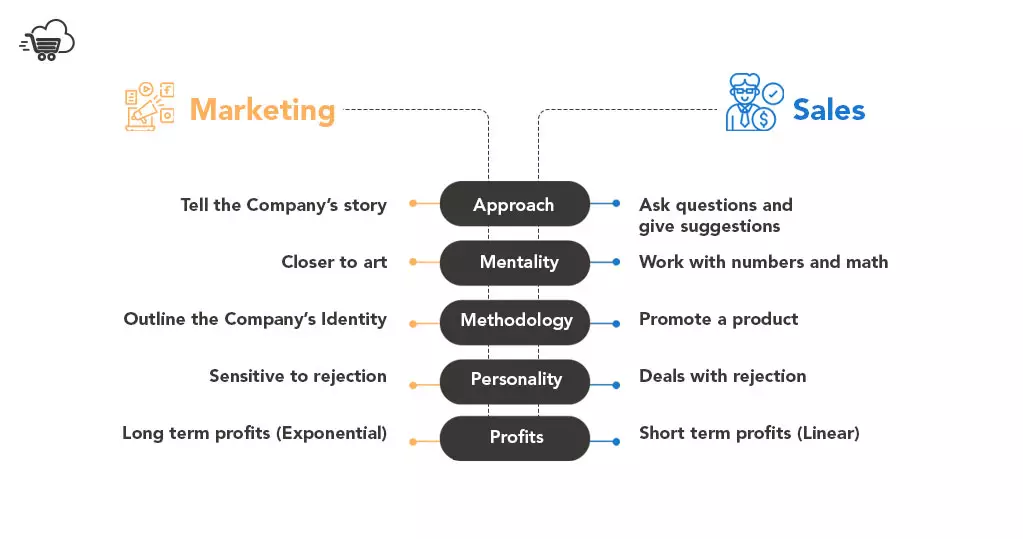
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Detail how you’ll reach your target audience. Will you focus on social media marketing, content marketing, or pay-per-click advertising? Explain your sales approach, pricing strategy, and how you’ll convert leads into customers.
Financial Projections
Include financial forecasts for the first few years of your business. Outline expected expenses, revenue, and profit margins. If you’re seeking funding, this section is crucial for demonstrating the financial viability of your business.
Choose Your Business Structure
Choosing the right legal structure for your business impacts everything from taxes to liability. Here are the most common options:
Sole Proprietorship
This is the simplest structure, ideal for solo entrepreneurs. It’s easy to set up and gives you complete control over your business. However, you’re personally liable for any debts or legal issues.
Partnership
A partnership is suitable if you’re starting the business with one or more partners. You’ll share profits, liabilities, and decision-making authority. It’s crucial to have a clear partnership agreement outlining roles, responsibilities, and profit sharing.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC offers the benefits of limited liability protection (separating personal assets from business liabilities) while maintaining flexibility in management and tax options. It’s a popular choice for small businesses.
Corporation
A corporation is more complex and is typically chosen by larger businesses. It offers strong liability protection but comes with stricter regulations and higher taxes. There are also subtypes like S-corporations and C-corporations, each with its own tax implications.
Register Your Business and Handle Legal Requirements
Once you’ve chosen your business structure, the next step is to legally register your business. This involves several steps, including registering your business name, obtaining licenses and permits, and setting up business accounts.
Register Your Business Name
Choose a unique name for your business and register it with the appropriate authorities. Make sure to check that the name isn’t already in use by another business. Registering your name gives you exclusive rights to use it and protects your brand identity.
Obtain Necessary Licenses and Permits
The types of licenses and permits you’ll need depend on your business and location. For example, a restaurant may require health permits, while a home-based business might need a general business license. Check with your local and state authorities to ensure compliance.
Get an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
An EIN is required for tax purposes and for hiring employees. You can obtain an EIN for free from the IRS website. It’s essentially your business’s Social Security number, used to identify your company for tax and legal purposes.
Open a Business Bank Account
Keep your personal and business finances separate by opening a dedicated business bank account. This will make managing your finances easier and provide a professional image to your customers.
Build Your Online Presence
In today’s digital world, having an online presence is crucial for any business. Even if you don’t sell products online, a professional website and active social media profiles can help establish credibility and attract customers.
Create a Professional Website
Invest in a user-friendly, mobile-responsive website that showcases your products or services. Include key information like your business’s story, contact details, and a blog for sharing valuable content. Consider using platforms like WordPress, Shopify, or Squarespace for easy website creation.

Set Up Social Media Accounts
Social media is a powerful tool for connecting with your audience, sharing updates, and promoting your business. Choose platforms that are relevant to your industry and target market. For example, Instagram is great for visual brands, while LinkedIn is ideal for B2B companies.
Optimize for SEO
Optimize your website and content for search engines by using relevant keywords, creating high-quality content, and building backlinks. Effective SEO strategies can help your business rank higher in search results, driving more organic traffic to your site.
Market and Launch Your Business
The final step is to introduce your business to the world. Create a buzz around your launch by using a mix of online and offline marketing strategies.
Leverage Social Media and Content Marketing
Announce your launch on social media and share engaging content that showcases your business’s value. Use a mix of posts, videos, and stories to capture attention and build anticipation.
Run Paid Advertising Campaigns
Consider using Google Ads, Facebook Ads, or Instagram Ads to reach a broader audience. Paid ads allow you to target specific demographics, interests, and behaviors, ensuring that your message reaches the right people.
Host a Launch Event
If applicable, host a virtual or in-person launch event to introduce your business. Offer special promotions, giveaways, or exclusive products to entice attendees and generate excitement.
Conclusion
Starting a business can be challenging, but with careful planning and determination, you can turn your idea into a successful enterprise. By following this step-by-step guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the startup process confidently. Remember, building a business is a marathon, not a sprint. Stay focused, be adaptable, and don’t be afraid to seek help and resources along the way. Good luck on your entrepreneurial journey!
FAQs
Do I need a business plan to start a small business?
Yes, a business plan is essential. It helps you outline your strategy, set clear goals, and demonstrate your business’s potential to investors or lenders.
What is the best business structure for a beginner?
For beginners, a sole proprietorship or LLC is often the best option due to its simplicity and minimal regulatory requirements.
How much does it cost to start a business?
Startup costs vary depending on the type of business. Typical expenses include licenses, equipment, marketing, and website creation. It’s important to create a budget and plan accordingly.
How can I protect my business idea?
Consider filing for trademarks, copyrights, or patents to protect your intellectual property. It’s also wise to use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) when discussing your idea with others.
What if my business idea doesn’t work out?
Not every idea will succeed, and that’s okay. Learn from your mistakes, refine your concept, and pivot if necessary. Many successful entrepreneurs have faced setbacks before finding success.
How do I know if my business idea is profitable?
Conduct market research to determine demand, set realistic financial projections, and test your product or service with a small audience to gauge interest before investing heavily.

